North Korean Hackers Use 500 Phishing Domains to Steal NFTs, Report Says
The company identified several traits of the phishing scams, including recording visitor data and requesting NFT item price lists.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
- Hackers linked to North Korea’s Lazarus Group are behind a phishing campaign targeting NFT investors and stealing their NFTs through fake websites.
- The campaign has used 500 domains and has been active for at least 7 months, according to blockchain security firm SlowMist.
- SlowMist identified several traits of the phishing scams, including recording visitor data and requesting NFT item price lists, and recommends users strengthen their security knowledge to avoid falling victim to such attacks.
Blockchain security firm SlowMist recently revealed that hackers linked to North Korea’s Lazarus Group are behind a massive phishing campaign that uses 500 domains to dupe victims and target their NFTs.
According to the security firm, North Korean Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group targets NFT investors and steals their NFTs through websites that disguise as a variety of NFT-related platforms and projects.
“Upon further investigation, we found that one of the techniques used in this phishing attack involved creating fake NFT-related decoy websites with malicious Mints. These NFTs were sold on platforms such as OpenSea, X2Y2, and Rarible,” SlowMist explained.

Recently, during the FIFA World Cup Championships, a site that pretended to be associated with it emerged. And as per the investigation of the firm, “by checking the registration information of these domain names, we found that the earliest registration date was traced back to 7 months ago.”
There were also four traits of these phishing scams as identified by the firm, namely:
- Phishing websites will record visitor data and save it to external sites. The hacker records visitors’ information to an external domain through an HTTP GET request. Although the domain names sending the request are different, the API interface of the request is “/postAddr.php”. The general format is “https://nserva.live/postAddr.php?mmAddr=…[Metamask]…&accessTime=xxx&url=evil.site”, where the parameter mmAddr records the visitor’s wallet address, and accessTime records the visitor’s visit Time, URL records the phishing website link currently visited by the visitor.
- The phishing website will request an NFT item price list, usually, the HTTP request path is “getPriceData.php”
- There is a file “imgSrc.js” linking images to the target project, which contains a list of target sites and the hosting location of the image files used on their corresponding phishing sites. This file may be part of the phishing site template.
- The main domain name used by APT to monitor user requests is “thedoodles.site,” which was mainly used to record user data in the early days of APT activities.
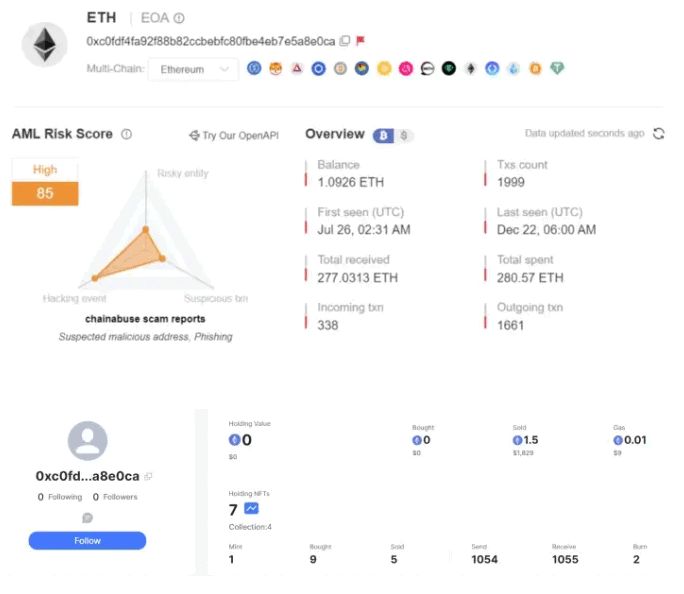
“The HTTPS certificate for this domain name was queried 7 months ago, indicating that the hacker organization had already begun targeting NFT users at that time,” SlowMist clarified.
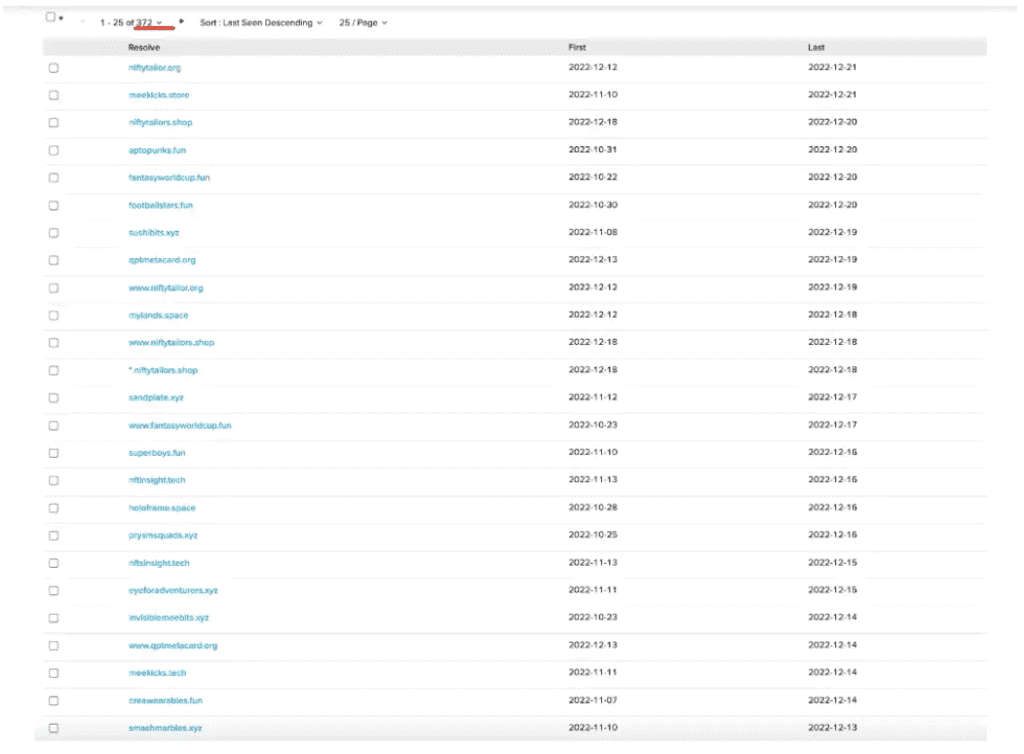
Though, according to the blockchain security firm, it cannot include all the information that their investigation has found out for privacy reasons, it also revealed that there are NFT phishing site groups under the same IP of the host, with 372 NFT phishing sites under a single IP and 20 NFT phishing sites associated under a different IP address.
“SlowMist advises users to strengthen their understanding of security knowledge and further enhance their ability to identify phishing attacks in order to avoid falling victim to such attacks. For additional security information, we recommend reading the ‘Blockchain Dark Forest Self-Help Handbook,’” SlowMist concluded.
This article is published on BitPinas: North Korean Hackers Use 500 Phishing Domains to Steal NFTs, Report Says
Disclaimer: BitPinas articles and its external content are not financial advice. The team serves to deliver independent, unbiased news to provide information for Philippine-crypto and beyond.





